SKOCH and Financial Inclusion
Today, Financial Inclusion is a term that comes easily to all politicians, policymakers, bureaucrats, civil society and other development organizations. It is a term that institutions and organizations are using to lend credibility to initiatives that only deal peripherally with what is the larger problem, that of 'mainstreaming the marginalised' and ensuring inclusive growth.
For us at SKOCH, it has been a 25 year-long journey, bringing to the forefront issues long before they became part of the official terminology, enabling institutions to form alliances that went a step forward in taking growth to the people, encouraging institutions to form alliances that went a step forward in taking growth to the people, encouraging cross-pollination of ideas and efforts that could allow governance to percolate to the grassroots; and form the springboard for economic inclusion. Scaling-up access to finance for India's rural poor presents a formidable developmental challenge in a country as vast and varied as India.
Financial Inclusion is not a one-off event. In terms of finance provision, it means that hitherto excluded people—either as individuals or as groups—now have access to credit on a regular basis for as long as they continue to abide by the terms of such a credit relationship. For financial inclusion to promote growth, it must move from “opening an account” in the bank, to regular savings and finally to a relationship which enables the borrower to access loans on a regular basis.
Financial Literacy goes beyond the provision of financial information and advice. The focus of any discussion on financial literacy is primarily on the individual, who usually has limited resources and skills to appreciate the complexities of financial dealings with financial intermediaries on a day-to-day basis.
Financial Deepening, encompassing credit and market penetration, is crucial from a financial sector. This involves addressing key economic needs such asproviding livelihood-linked credit and ensuring lower-risk market penetration to protect against inflation. Achieving digital transformation at a large scale is also necessary. Financial Deepening is essential for promoting and accelerating economic growth by mobilizing savings and allocating them effectively for development.
It is measured by the relative size of the financial sector, including banks, financial institutions, and markets, compared to the overall economy. This is because of the central role of the financial system in mobilising savings and allocating the same for the development process. The variable is defined as domestic private credit to the real sector by deposit money banks as percentage of local currency GDP. The private credit, therefore, excludes credit issued to governments, government agencies, and public enterprises. It also excludes credit issued by central banks. The size of stock markets is approximated by stock market capitalization to GDP, while the outstanding volume of private debt securities to GDP is commonly used as a proxy for the size of bond markets. The combined measure of these two indicators provides a rough indication of the relative size of financial markets. Since the major role of the financial system is the transfer of funds from the surplus sector to the deficit sector, one way of judging efficiency is to determine how well this intermediation function is performed.
SKOCH Group has been working in the field of Financial Inclusion, Financial Literacy and Financial Deepening since inception in 1997.
A brief history of our work in this area is given below:

Our main aim is to make one woman in each Gram Panchayat financially and digitally literate. The programme aims at financial inclusion with special emphasis on women contrary to other financial inclusion schemes, which have not adequately focused either on financial literacy or on women who have a much more pronounced need to save. It also does not limit the financial inclusion vision to mere opening of no-frill accounts that no one uses.
CIO Agenda Task Force Roundtable on Financial Deepening
Key Recommendations:
- Expand Mutual Funds to promote financial inclusion.
- AI-backed self-service products for small and medium investors.
- Investment protection for the lower to middle class can be enhanced through Gold/Silver ETFs and Index Funds.
- Innovations are essential for financial inclusion.
- Wider debt market is necessary to support large industries and SMEs.
- Regulatory oversight of innovations to ensure efficiency without becoming overly restrictive.
- Documenting the Total Economic Impact (TEI) of IT.
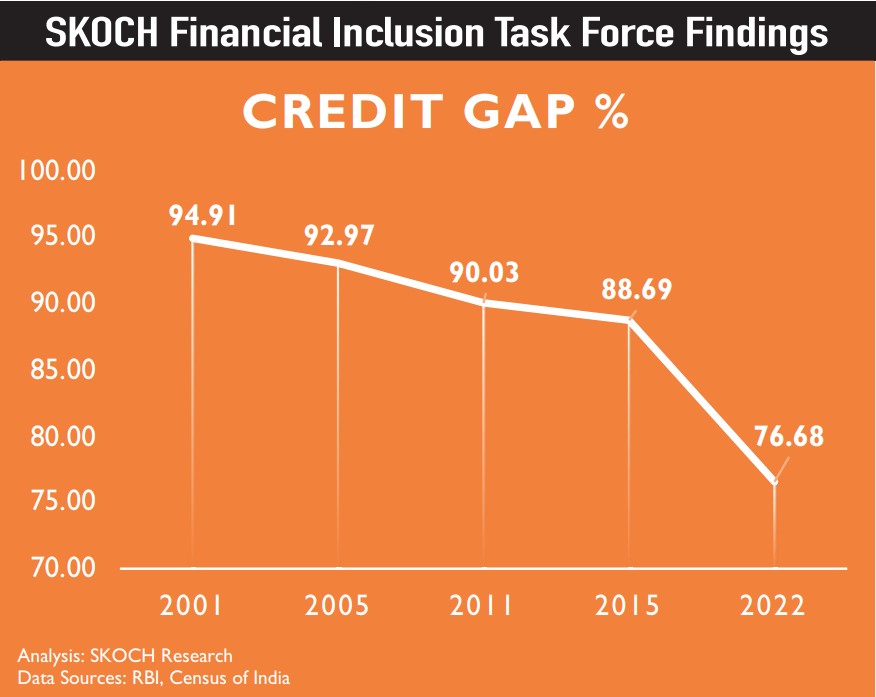
Financial Inclusion Task Force (FITF) Findings: Credit gap falls 12.01 percent
In 2023, SKOCH Group released research that found that the Credit Gap in India has fallen 12.01% percentage points in seven years between 2015 & 2022 as against a mere 6.22 percentage point drop in the previous 14 years between 2001 and 2015, showing impressive outcome of the Financial Inclusion initiatives taken by the Prime Minister Narendra Modi government according to a report released by the SKOCH Financial Inclusion Task Force ahead of the Union Budget 2023-24.
Learn More
Financial Inclusion Task Force (FITF)
In 2022, SKOCH Group has formed a Financial Inclusion Task Force (FITF) under the aegis of the SKOCH Development Foundation and the CEO's Association for Inclusive Growth (CAII) to return recommendations on digital lending and markets - bridging credit & literacy gaps.

Learn More
National Multi-Institutional Survey on MSMEs in India
In 2020, SKOCH Group released a three-part report titled 'National Multi-Institutional Survey on MSMEs in India' which looked at credit availability to the MSME sector.
SKOCH Samavesh Financial Literacy Programme in Bijnor, Uttar Pradesh

SKOCH Samavesh Financial Literacy Programme in Muzaffarpur, Bihar

PMJDY Drives Financial Inclusion Home: A Performance Analysis of PMJDY
In 2018, SKOCH Group released a national study 'PMJDY Drives Financial Inclusion Home: A Performance. From a poorly banked to an almost universally banked country at the household level is the most laudable achievement of the Financial Inclusion (FI) initiatives of the government since 2014. Financial inclusion gets a big push under Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY), wherein 34 crore Financial Inclusion accounts have been added in the largest concerted effort ever to push the total number of FI accounts to 58.3 crores that serve the purpose of FI.
Based on the SKOCH Sample Data, the six sampled banks had a total of 18.11 crore Financial Inclusion accounts in December 2017, up from 4.16 crore Financial Inclusion Accounts in March 2014—an increase of 4.35 times.
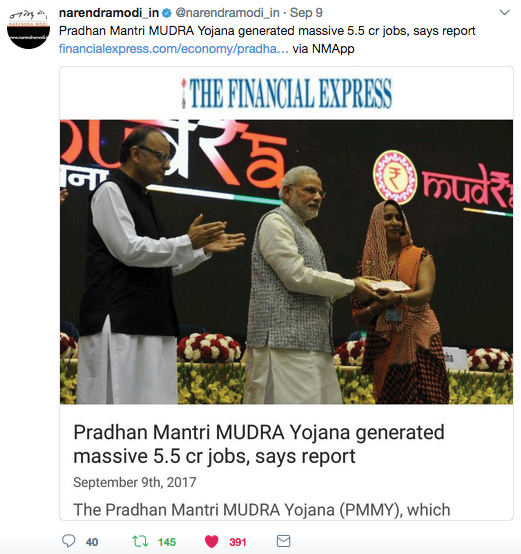
National study on Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana
In 2017, SKOCH released a national study on Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana which measured the impact of MUDRA loans on job creation in India that was tabled in the Parliament of India by the Minister of State for Finance and shared on social media by Prime Minister Modi.
Defeating Poverty: Jan Dhan and Beyond
was released that looked at the Jan-Dhan, Aadhar, and Mobile (JAM) Trinity and how it could be leveraged for alleviating poverty in India. It suggested several policy prescriptions for the BFSI sector to be able to leverage Financial Access for Financial Inclusion that have since been successfully implemented.


Learn More
SKOCH Samavesh Financial Literacy Programme was organised in Pilibhit, Uttar Pradesh

SKOCH Samavesh Financial Literacy Programme in Gandhinagar, Gujarat

SKOCH Samavesh Financial Literacy Programme in Dehradun, Uttarakhand

Speeding Financial Inclusion
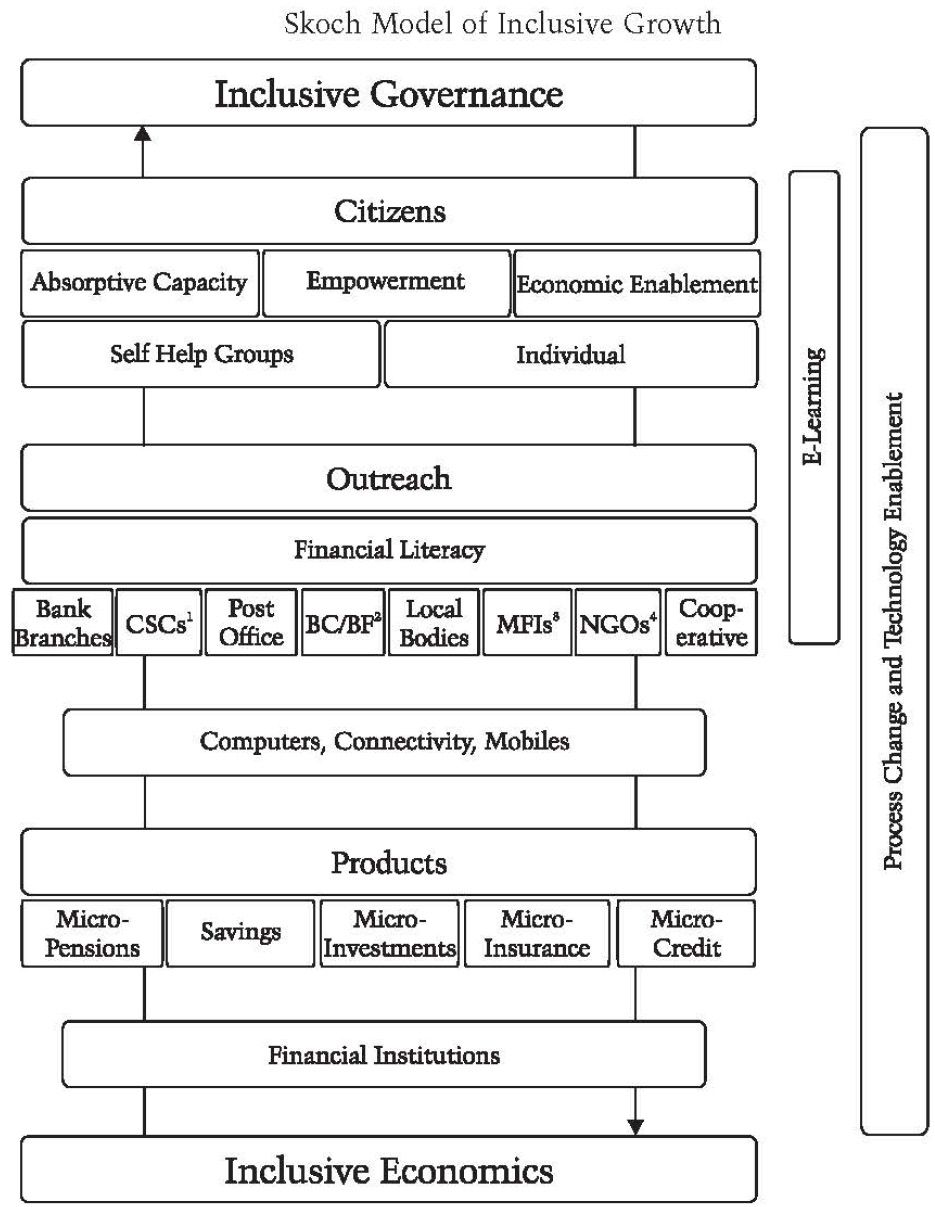
formalised the idea of Inclusive Economics, Inclusive Governance and gave the SKOCH Model of Inclusive Growth. This volume looked at the needs of the poor and the reality of financial exclusion, role of microfinance, demand-side factors, role of RBI, cost of financial access and converting Financial Access to Financial Inclusion.
Financial Deepening
With Finance Minister Pranab Mukherjee spearheading the policy initiative, there is swell of opinion that a high level of financial deepening is a necessary condition for accelerating and sustaining growth in the economy. To bring about inclusive growth, this translates into urgent action on the financial inclusion front, Team Inclusion reports.
Financial Inclusion, published by SKOCH Group
The compilation focused on various facets of financial inclusion ranging from opening up of no-frills accounts to micro-credit to financial literacy, while emphasising the role of process changes, technology enablement, capacity building, and outreach mechanism. It proposed a model of inclusive development, emphasising that inclusive economics leads to inclusive development.

Financial InclusionEditors: Sameer Kochhar
R. Chandrashekhar
K.C. Chakrabarty
B. Phatak
(2008)
The objective of financial inclusion is to extend the scope of activities of the organised financial system to include within its ambit people with low incomes. Through graduated credit, the attempt must be to lift the poor from one level to another so that they come out of poverty.
The Modi Government has laid the necessary infrastructure and made considerable progress to make this happen. It has achieved the objective of universal banking. DBT has been a great success. Over six crore PMJDY account holders have received DBT from various schemes. The beginning was made on 15th August 2014, when the Hon'ble Prime Minister announced PMJDY to fulfill the objective of universal financial inclusion taking banking to the last mile.
SKOCH Model of Inclusive Growth featured for the first time in the book, Financial Inclusion (2008) and shortly followed in the next book, Speeding Financial Inclusion (2009). These books had a pronounced policy impact. Most recommendations were accepted and implemented. ModiNomics (2014) again argued for inclusive economics and inclusive governance as per Modi Ji's Gujarat model.
The third book Defeating Poverty: Jan Dhan and Beyond (September 2014) contributed to the current spate of policy interventions like DBT, MUDRA, overdraft in Jan Dhan accounts and Payments. The roadmap for public digital infrastructure for financial inclusion was laid out in Modi's Odyssey: Digital India, Developed India (2016).
We have formed a Financial Inclusion Task Force (FITF) under the aegis of the SKOCH Development Foundation and the CEO's Association for Inclusive Growth (CAII) to return recommendations on digital lending and markets - bridging credit & literacy gaps.






 and
and 

















